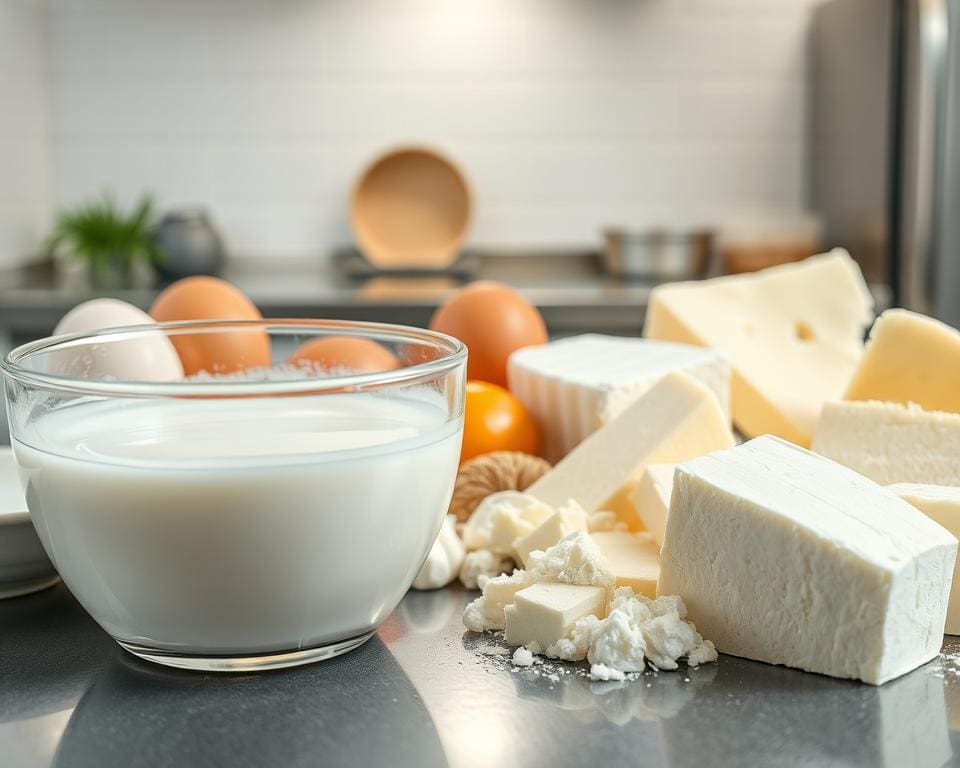
Coagulation is a pivotal process in food technology, fundamentally transforming liquid components into a semi-solid or solid state. This intricate Food Technology Coagulation mechanism plays a crucial role in a plethora of culinary applications, including the creation of cheese and the formation of custards. At its core, the coagulation process revolves around understanding proteins, which are essential to this transformation. When subjected to heat, acidity, or enzymes, proteins unfold and aggregate, resulting in a thickened liquid that enhances food texture and stability. A thorough exploration of coagulation unveils the secrets behind achieving desired shapes, forms, and mouthfeel in culinary creations.
Definition of Coagulation
Coagulation signifies a crucial transformation in food preparation, essential for achieving desired textures and structures. This process entails the conversion of a fluid into either a solid or semi-solid state, making it a fundamental aspect of both culinary science and food chemistry.
Understanding Coagulation in Culinary Science
In coagulation in culinary science, chefs harness this process to create a variety of dishes and food products. A prime example is cheese-making, where milk proteins curdle due to the addition of rennet or acid. This transformation not only creates the consistency needed for cheese but also influences its flavour profile. Mastering this technique allows culinary professionals to innovate and refine their recipes, offering unique texture experiences to diners.
The Role of Coagulation in Food Chemistry
From the standpoint of coagulation in food chemistry, understanding the underlying reactions is vital. These reactions modify protein structures, which directly impacts emulsification and gel formation. This knowledge empowers food technologists to manipulate ingredients effectively, ensuring that nutritional properties and textures are optimised in various food products. Emphasising the scientific approach to coagulation facilitates the creation of more stable, appealing, and nutritious food items.
What Is Coagulation In Food Tech
The process of coagulation in food technology holds significant importance in culinary practices. Understanding what this entails can elevate food preparation techniques and enhance flavour profiles. The coagulation process is vital for creating the desired texture and consistency in various dishes.
The Importance of Coagulation in Food Preparation
Coagulation serves as a fundamental element in food preparation, affecting the outcome of numerous recipes. When proteins in ingredients undergo coagulation, they form a structured network that can trap moisture and contribute to the overall mouthfeel. Employing effective coagulation methods allows chefs to achieve consistent results, whether it’s turning milk into cheese or producing a velvety sauce.
How Coagulation Affects Texture and Flavour
The interaction between proteins during the coagulation process not only influences texture but also plays a critical role in flavour development. For example, when cooking meats, the heat causes proteins to coagulate and caramelise, producing a rich, savoury taste. This transformation showcases how integral coagulation is in crafting delicious and satisfying meals.
Coagulation Process and Mechanism
The coagulation process is a fundamental aspect of culinary science, shaping the texture and consistency of various foods. Understanding the steps involved in this process illuminates the intricate interactions among proteins during food preparation. The coagulation mechanism showcases how physical and chemical changes play a pivotal role in transforming ingredients into appealing dishes.
Step-by-Step Overview of the Coagulation Process
The coagulation process can be understood in phases, beginning with the denaturation of proteins. In this initial step, proteins unfold, a reaction often induced by heat or acidity. Following denaturation, proteins aggregate, resulting in the formation of clumps as they bond together. Techniques such as whisking egg whites exemplify this process, incorporating air that contributes to foaming and thickening. As proteins continue to aggregate, a series of changes unfolds.
Physical and Chemical Changes During Coagulation
During coagulation, significant physical changes occur, notably alterations in texture. The transformation from a fluid to a solid state represents one of the physical changes during coagulation. Chemical interactions, such as the establishment of cross-links between protein molecules, contribute to the solidified structure of the food. Understanding these changes is crucial for refining food products, both in home cooking and commercial food production.
Types of Coagulation
Understanding the various types of coagulation is crucial for anyone involved in food technology and culinary arts. Different coagulation methods serve distinct purposes, and each has unique applications in food preparation. This knowledge enhances a chef’s ability to create textures and flavours that delight the palate.
Different Coagulation Methods in Food Tech
Several coagulation methods are prevalent in the culinary world. Each method has its own set of characteristics and applications:
- Thermal Coagulation: This method involves applying heat to proteins, resulting in firm structures as seen in cooked eggs or seared meats.
- Acid-Induced Coagulation: Commonly used in cheese making, this method involves adding acidic substances like vinegar or lemon juice to cause proteins to curdle.
- Enzymatic Coagulation: Often found in gelatine products, enzymes facilitate the coagulation process, resulting in a gel-like consistency.
Examples of Coagulation in Various Foods
Examples of coagulation in foods demonstrate the versatility of these techniques. Notable instances include:
- The formation of curds during cheese production.
- The setting of custards and puddings, which rely on cooking methods that involve thermal coagulation.
- The delicate structure of panna cotta, showcasing the result of enzymatic coagulation.
Coagulation in the Food Industry
Coagulation plays a pivotal role in the food industry, significantly influencing product stability, texture, and overall quality. In the context of Food Technology Coagulation, this process ensures the consistent standardisation of a myriad of products, including dairy items, desserts, and meat alternatives. When manufacturers optimise the coagulation process, they can achieve the desired characteristics across mass-produced items, thereby enhancing consumer satisfaction and safety.
Take cheese production, for example, where the meticulous control of coagulation temperature and pH levels is vital. The precision involved in these factors not only determines the texture but also the flavour profile of the final product. As the food industry continually evolves, advancements in food science unveil new insights that further refine the coagulation process, leading to innovative breakthroughs in product development, such as alternative dairy solutions and plant-based foods.
Understanding the implications of coagulation in the food industry is essential. By integrating these insights into product development strategies, businesses are well-placed to meet the increasing consumer demand for quality and reliability. Ultimately, embracing the science behind coagulation enhances the overall integrity of food products, reaffirming the industry’s commitment to excellence.









